What is Penetration Grade Bitumen
It is created by forcing air through liquid bitumen, which causes it to harden into a form with a high penetration value (a gauge of the substance’s hardness). Hot mixBitumen commonly contains penetration bitumen as a binder and a waterproofing substance. It is the best product to use in cold weather and in regions with high traffic because of its low viscosity and high penetration value.
Bitumen (often referred to as asphalt) is categorized using the penetration grade system according to how hard or viscous it is. The depth to which a standard needle (with a 1/10 inch2 circular cross-section) penetrates into a sample of bitumen at a certain temperature (usually 25 or 60 degrees Celsius over a specified period of time) determines the penetration grade (typically 5 or 10 seconds).
The amount of tenths of a millimeter that the needle penetrates the bitumen is used to describe the penetration grade. For instance, a penetration grade of 40 indicates that the needle penetrates the bitumen by 40 tenths of a millimeter. The bitumen becomes softer and more viscous as the penetration grade increases.
What does Penetration Grade 30/40 mean?
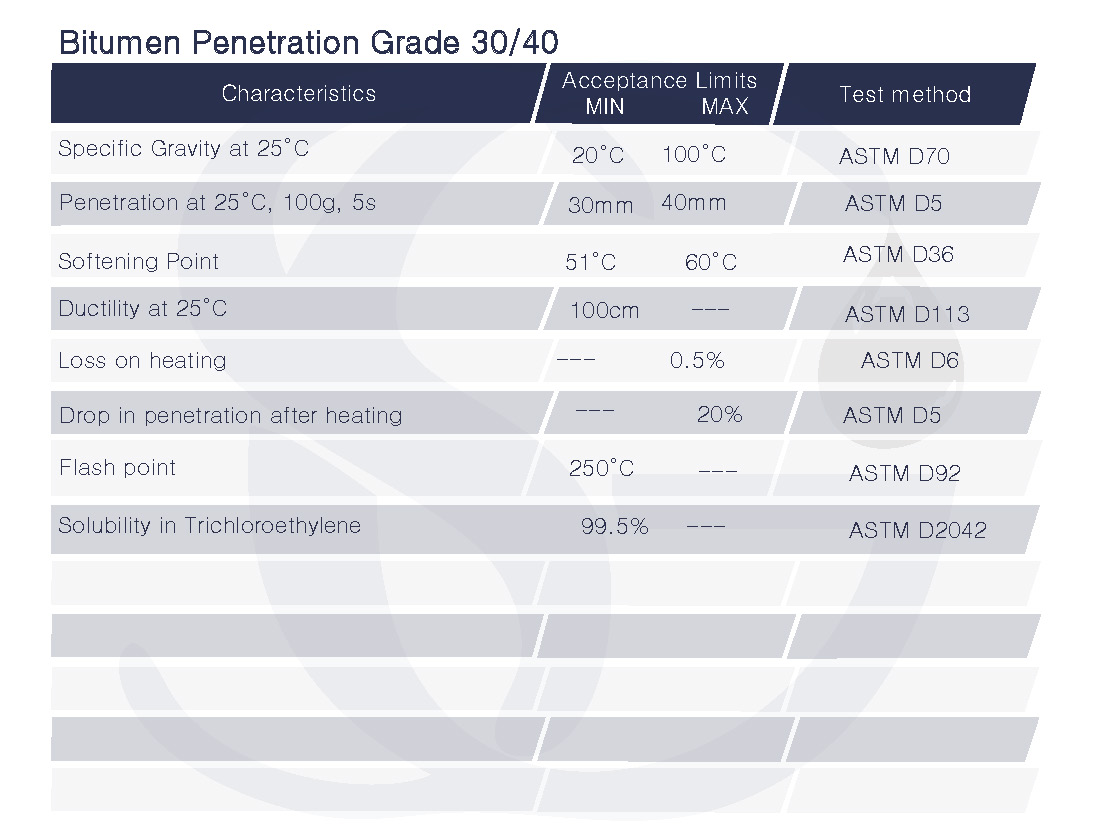
The bitumen has a penetration value between 30 and 40 decimillimeters, according to the bitumen penetration grade 30/40. (0.3 to 0.4 millimeters). This kind of bitumen is regarded as medium-grade bitumen and is appropriate for a number of uses, such as waterproofing, insulation, and road building.
In tropical regions, this grade of bitumen is one of the most popular ones for road building.
Bitumen Penetration Grade 40/50
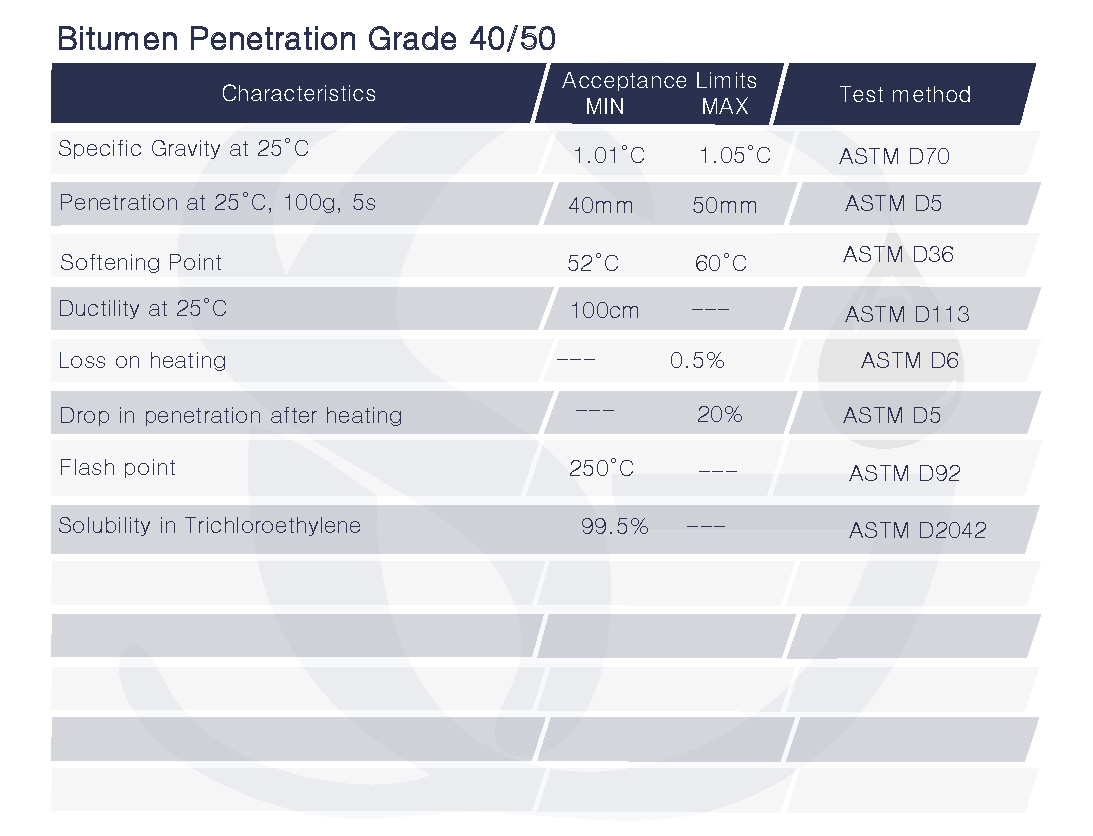
The bitumen has a penetration value between 40 and 50 decimillimeters, according to the bitumen penetration grade 40/50. (0.4 to 0.5 millimeters). This kind of bitumen is regarded as a medium-hard grade that may be used for a number of tasks, such as insulating, waterproofing, and building roads.
Bitumen Penetration Grade 40/50 is better suited for applications that call for a tougher, more durable bitumen since it has a greater viscosity and is harder than Bitumen Penetration Grade 30/40.
Application use of Bitumen Penetration Grade 40/50
Road construction: Bitumen Penetration Grade 40/50 is often used in the construction of roads and highways, as it provides a strong and durable surface that can withstand heavy traffic and harsh weather conditions.
The bitumen has a penetration value between 50 and 70 decimillimeters, according to the bitumen penetration grade 50/70. (0.5 to 0.7 millimeters). This kind of bitumen is regarded as a hard grade bitumen that may be used in a number of applications, such as insulating, waterproofing, and road construction.
Bitumen Penetration Grade 50/70 is better appropriate for applications that call for a highly hard and durable bitumen since it has a greater viscosity and is tougher than Bitumen Penetration Grade 40/50.
A sort of bitumen known as Bitumen Penetration Grade 50/70 is defined by its viscosity or consistency, as determined by its penetration value. This hard grade bitumen is appropriate for a wide range of applications that require durable substance.
How is Penetration Bitumen 60/70 made?
The production process of Bitumen Penetration Grade 60/70 typically involves the following steps:
- Crude oil refinement: The crude oil is first refined to separate different components, such as gasoline, diesel, and kerosene.
- Vacuum distillation: The residual crude oil is then subjected to vacuum distillation to separate out the bitumen.
- Blowing process: The resulting bitumen is then subjected to a blowing process, in which air is blown into the hot bitumen to create small bubbles. This increases the volume of the bitumen and reduces its viscosity.
- Refining: The bitumen is then refined to produce Bitumen Penetration Grade 60/70 by controlling the temperature, pressure, and composition of the bitumen during the refining process.
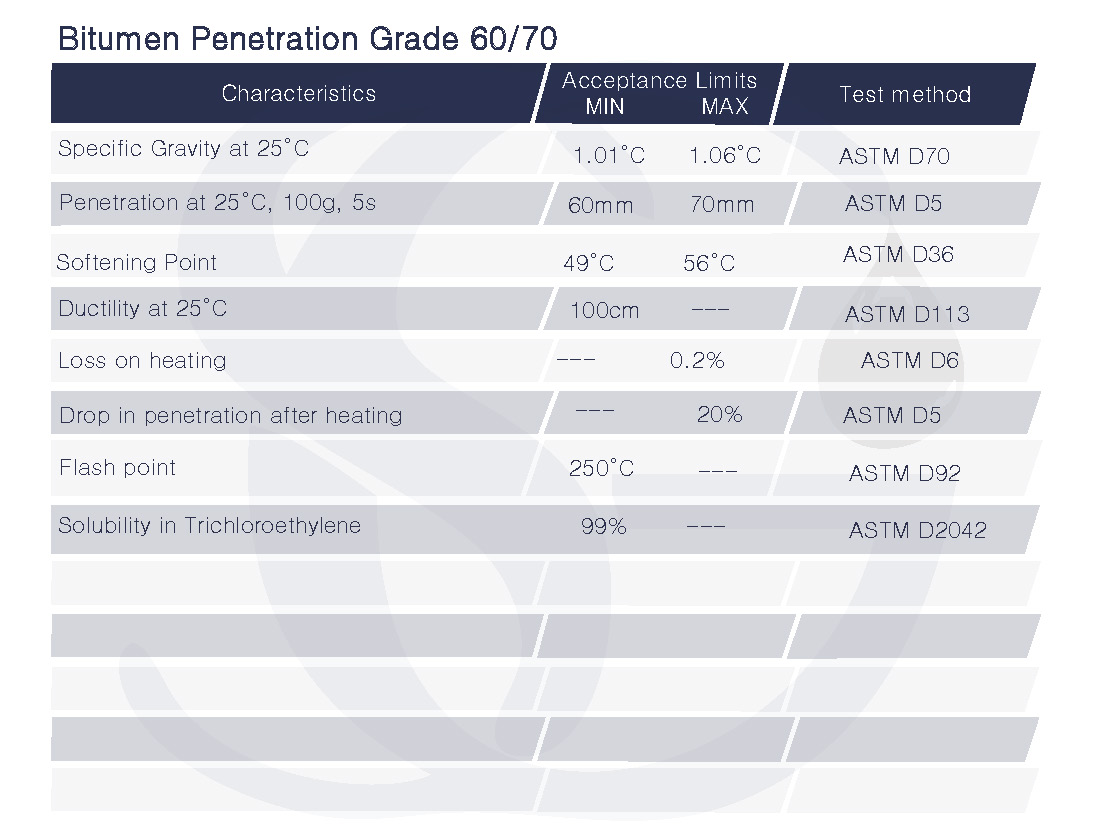
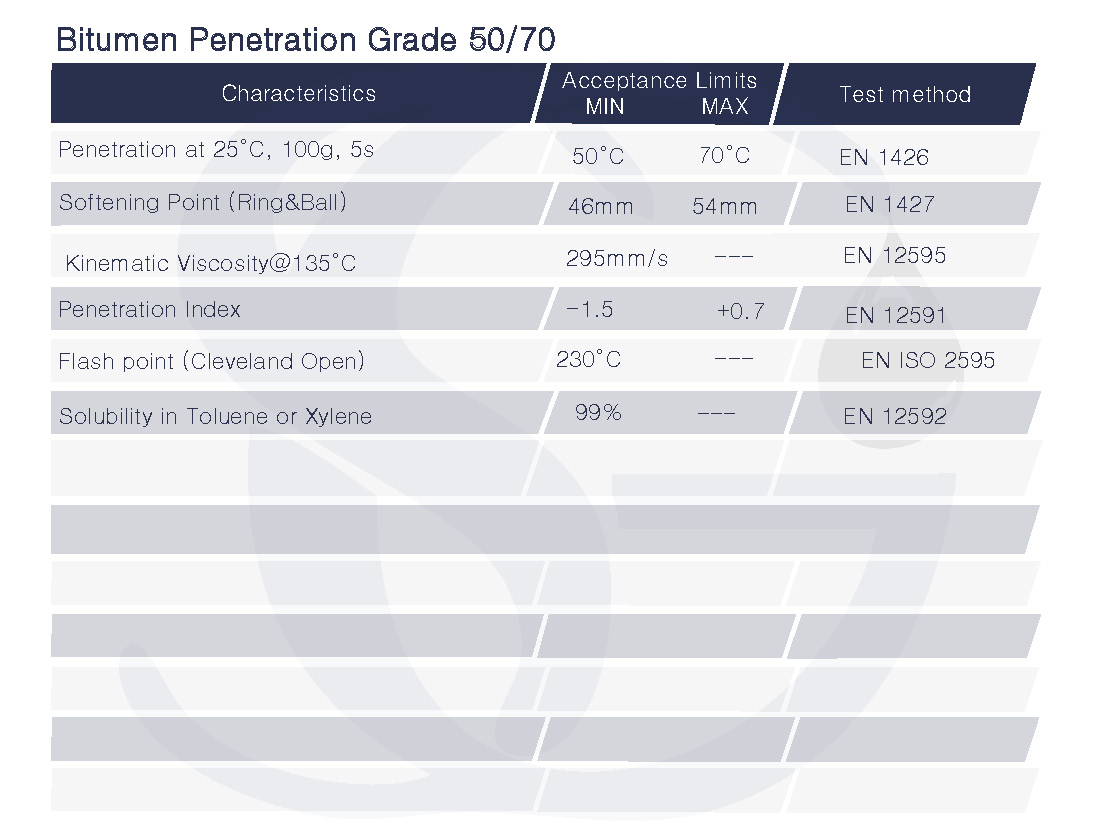
- Testing and quality control: The resulting bitumen is then subjected to various tests, such as penetration testing, softening point testing, and viscosity testing, to ensure that it meets the specifications for Bitumen Penetration Grade 60/70. Defination of Penetration Grade 60/70The bitumen’s viscosity in hundredths of a millimeter (mm) at 60 degrees Celsius (140°F) is indicated by the numerals 60/70. With a penetration value of 60 at 25°C (77°F) and a penetration value of 70 at 60°C (140°F), bitumen with a penetration grade of 60/70 is considered to be of medium quality.In order to build roads and highways, bitumen penetration grade 60/70 is frequently employed because to its excellent weather resistance and capacity to function effectively in a variety of temperature ranges. It is also employed as a binder in asphalt concrete mixtures and in the production of bituminous waterproofing membranes.

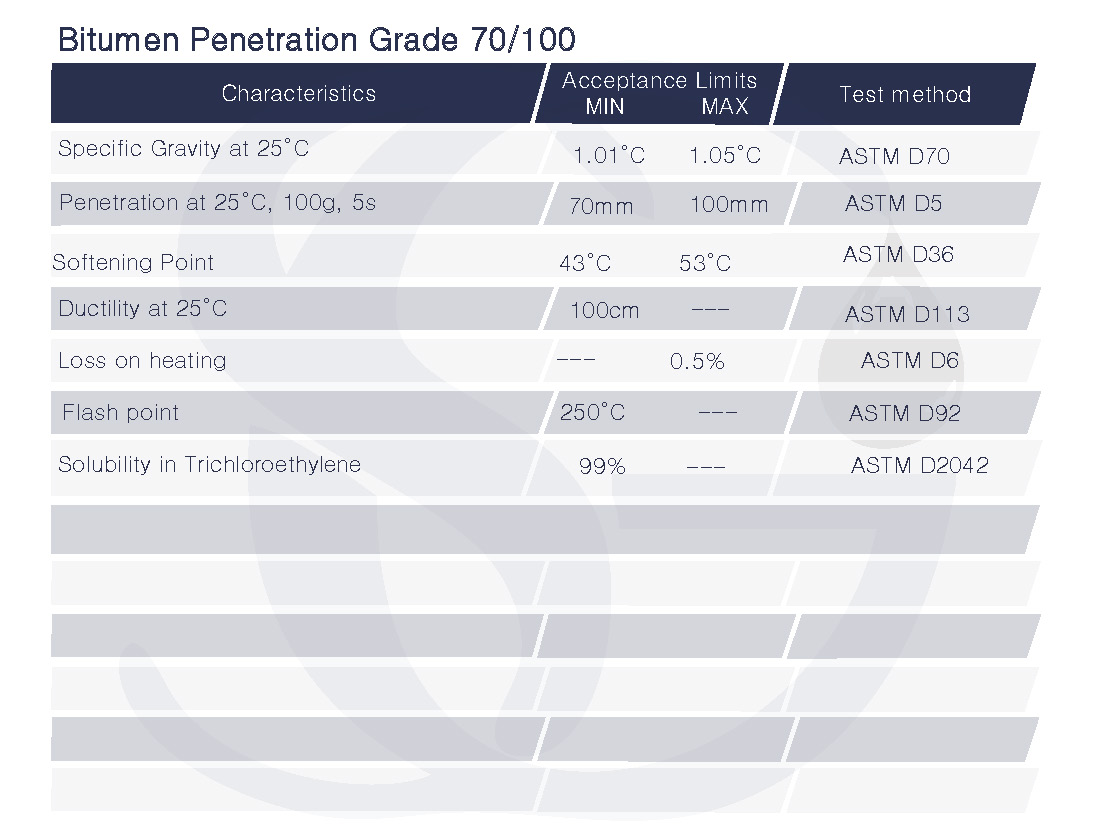
The numbers 80/100 indicate the viscosity of the bitumen in hundredths of a millimeter (mm) at 60 degrees Celsius (140°F). Bitumen with a penetration grade of 80/100 means that it has an even higher viscosity compared to bitumen with a penetration grade of 70/100. It has a penetration value of 80 at a temperature of 25°C (77°F) and a penetration value of 100 at a temperature of 60°C (140°F).
Mostly used in the construction of roads and highways in regions with extremely harsh climates and temperatures.
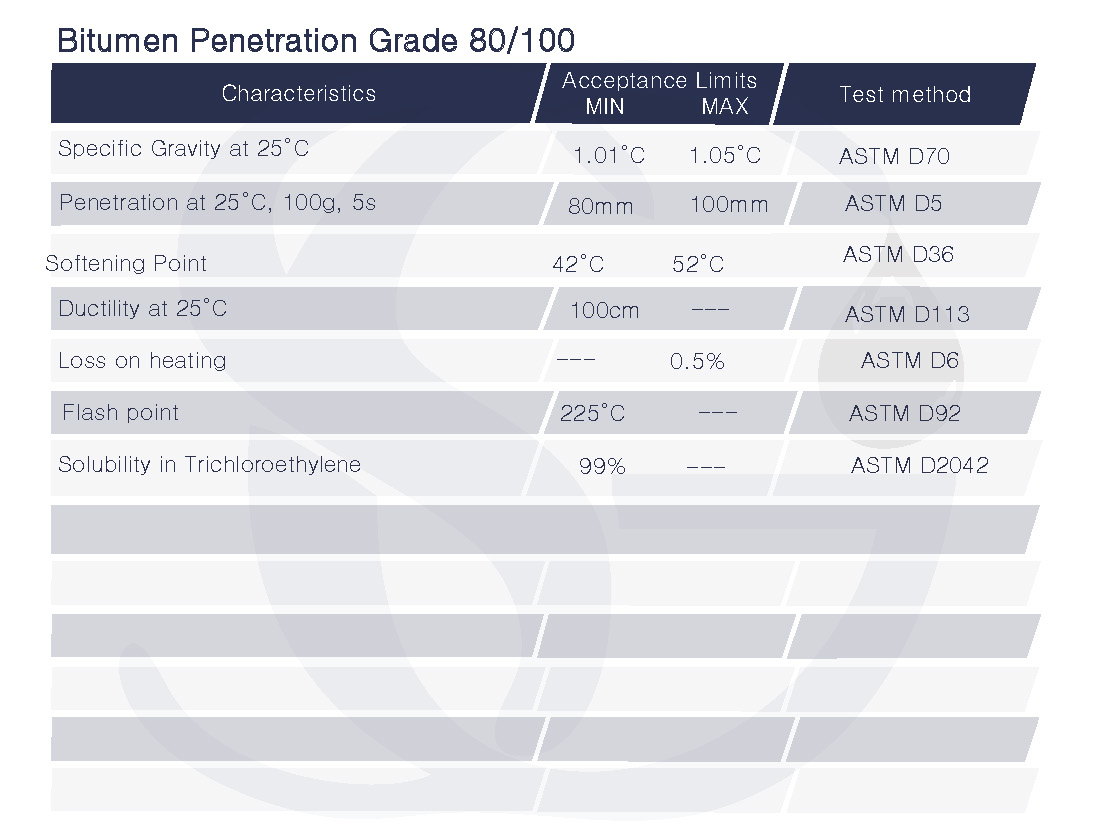
The bitumen’s viscosity at 60 degrees Celsius (140 degrees Fahrenheit) is shown by the ratio 85/100 in hundredths of a millimeter (mm). When bitumen has an 85/100 penetration grade, it has an even greater viscosity than bitumen with an 80/100 penetration grade. At 25 °C (77 °F), it has a penetration value of 85, and at 60 °C (140 °F), it has a penetration value of 100.
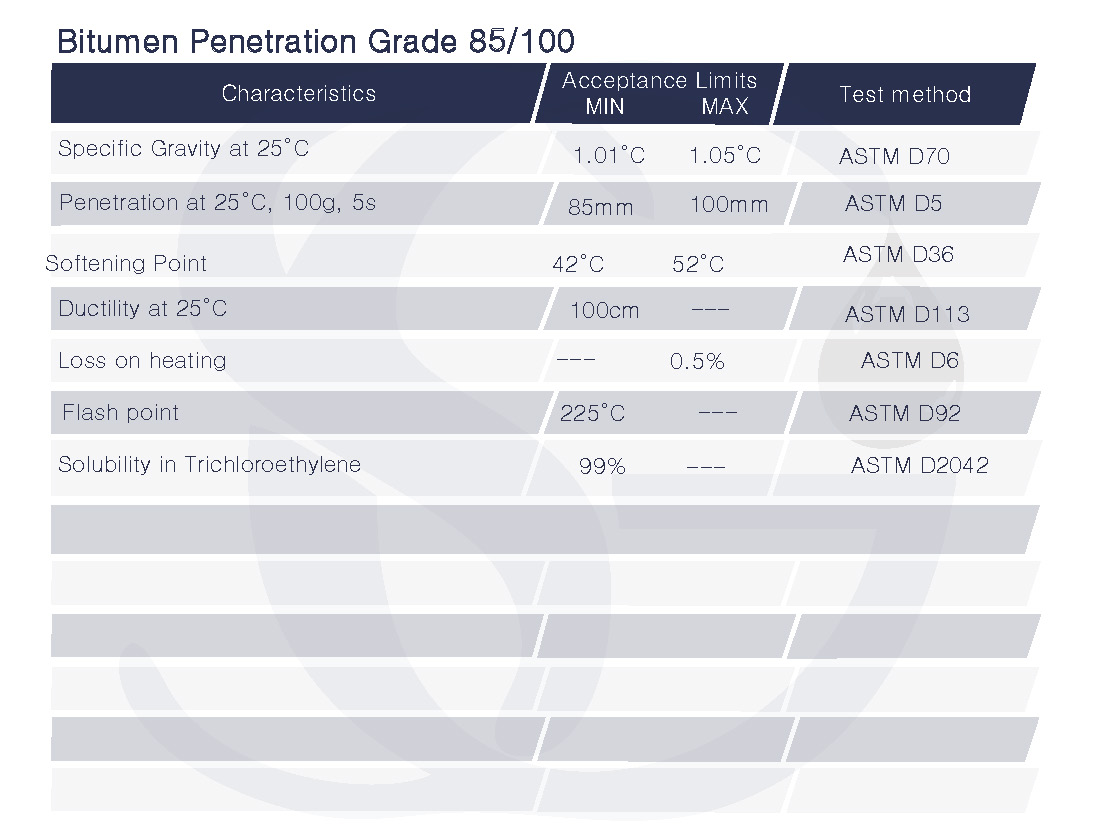
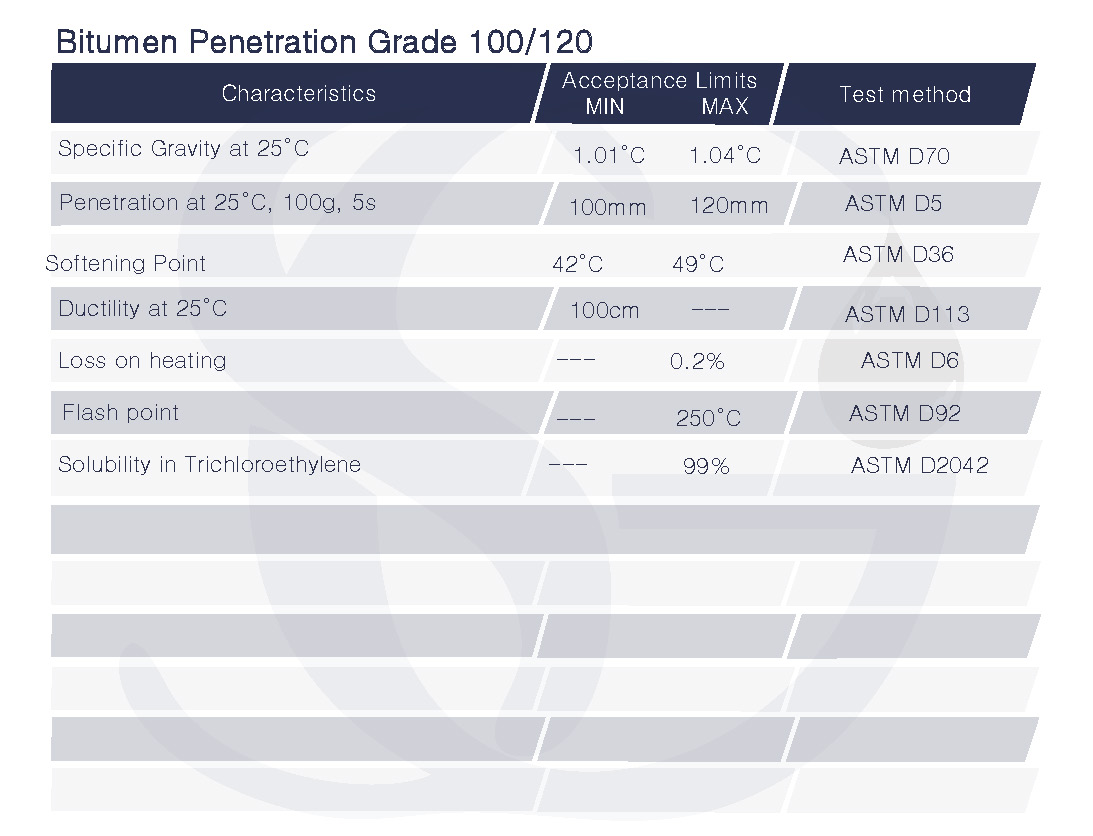
The bitumen’s viscosity at 60 degrees Celsius (140 degrees Fahrenheit) is shown by the digits 100/120 in hundredths of a millimeter (mm). When compared to other bitumen grades, bitumen with a penetration grade of 100/120 has an extremely high viscosity. At a temperature of 25 °C (77 °F), it has a penetration value of 100, and at a temperature of 60 °C (140 °F), it has a penetration value of 120.